Description
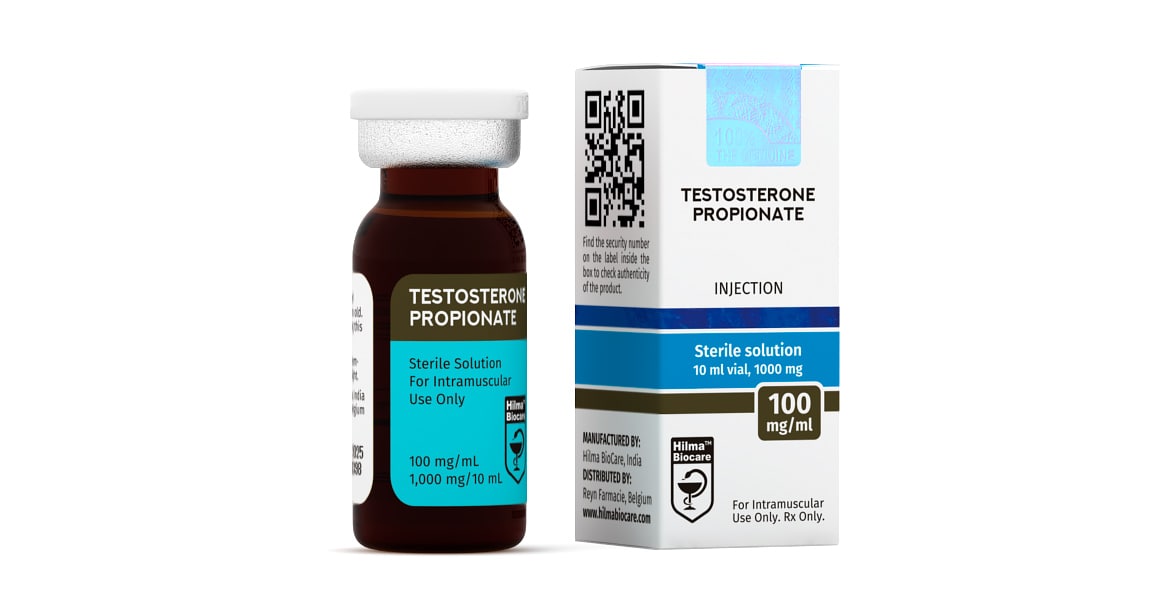
Testosterone Propionate
Strength: 100mg/ml
Molecular Formula: C22H32O3
Molecular Weight: 344.48768 g/mol
Active Ingredient: Testosterone propionate
CAS number: 57-85-2
Dosage Form: Injectable, oil base sterile solution
Route: Injection
Market Status: Prescription
Company: Hilma Biocare
DESCRIPTION
Testosterone Propionate 100 is an oil based solution of testosterone propionate for IM
injection designed to reach peak testosterone serum levels within 24 hours of IM
administration and remain elevated for 2 to 3 days. Testosterone propionate 100 is suitable
for the treatment of hypogonadism and other disorders related to androgen deficiency.
Testosterone Propionate 100 has both anabolic and androgenic effects. Testosterone
supplementation has been demonstrated to increase strength and growth of new muscle
tissue, frequently with increases in libido.
INDICATIONS
Adult Males: Testosterone Propionate 100 Injection is indicated for replacement therapy in
conditions associated with deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone. Primary
hypogonadism: Testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing
testis syndrome, or orchidectomy. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: idiopathic gonadotropin
or LHRH deficiency, or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone are responsible for normal growth and development
of the male sex organs and for maintenance of secondary sex characteristics. These effects
include the growth and maturation of the prostate, seminal vesicles, penis, and scrotum; the
development of male hair distribution, such as facial, pubic, chest, and axillary hair; laryngeal
enlargement; vocal cord thickening; alterations in body musculature: and fat distribution and
have been reported to stimulate the production of red blood cells by enhancing the
production of erythropoietic stimulating factor. Male hypogonadism results from insufficient
secretion of testosterone and is characterized by low serum testosterone concentrations.
Symptoms associated with male hypogonadism include decreased sexual desire with or
without impotence, fatigue and loss of energy, mood depression, ‘ regression of secondary
sexual characteristics, and osteoporosis. Hypogonadism is a risk factor for osteoporosis in
men. Androgens have been reported to increase protein anabolism and decrease protein
catabolism. Nitrogen balance is improved only when there is sufficient intake of calories and
protein. During exogenous administration of androgens, endogenous testosterone release
may be inhibited through feedback inhibition of pituitary luteiniz-ing hormone (LH). At large
doses of exogenous androgens, spermatogene-sis may also be suppressed through
feedback inhibition of pituitary follicle- stimulating hormone (FSH). Esterification of
testosterone at position 17 increases the lipid solubility of the testosterone molecule and
prolongs the activity of the molecule by increasing its residence time. Following
intramuscular administration in an oily vehicle, testosterone ester is slowly absorbed into the
circulation and rapidly hydrolysed in plasma to testosterone. Circulating testosterone is
chiefly bound in the serum to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin.
Testosterone is metabolized to various 17-ketosteroids through two different pathways. The
major active metabolites of testosterone are estradiol and dihydrotestosterone. Testosterone
is metabolized to DHT by steroid 5-alpha reductase located in the skin, liver, and the
urogenital tract of the male. DHT binds with greater affinity to SHBG than does testosterone.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Male: Gynecomastia, excessive frequency and duration of penile erections, oligospermia.
Skin and Appendages: Hirsutism, male pattern baldness and acne, gynecomastia.
Fluid/electrolyte Disturbances: Retention of sodium, chloride, water, potassium, calcium, and
inorganic phosphates.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, cholestatic jaundice, alterations in liver function tests; rarely,
hepatocellular neoplasms, peliosis hepatitis, hepatic adenomas, and cholestatic hepatitis.
Hematologic: Suppression of clotting factors II, V, VII, & X;bleeding in patients on anticoagulant therapy.
Nervous System: Increased or decreased libido, headache, anxiety, depression, and
generalized paresthesia.
Other: Serum lipid changes, hypercalcaemia, hypertension, oedema, priapism, and
potentiation of sleep apnea.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients with known hypersensitivity to any ingredients in this product. Patients with known
or suspected carcinomas of the breast, testis, or prostate. Patients with severe heart
disease, liver disease, or kidney disease or with a history of epilepsy. Products containing
testosterone 1, should not be used in women as they may cause virilization and fetal harm.
PRECAUTIONS
Because androgens may alter serum cholesterol concentration, caution should be used
when administering these drugs to patients with a history of myocardial infarction or coronary
artery disease. Patients on oral anticoagulant therapy require close monitoring especially
when androgens are started or stopped. Diabetics: androgens may alter the metabolism of
oral hypoglycemic agents or may change insulin sensitivity in patients with diabetes mellitus
which may require adjustment of dosage of insulin and other hypoglycemic drugs.
PATIENT MONITORING
Serum Cholesterol, HDL, LDL, TG. Hemoglobin and Hematocrit, Hepatic function tests –
AST/ALT Prostatic specific antigen – PSA, Testosterone: total, free, and bioavailable.
Dihydrotestosterone & Estradiol. Male patients over 40 should undergo a digital rectal
examination and evaluate PSA prior to androgen use. Periodic evaluations of the prostate
should continue while on androgen therapy, especially in patients with difficulty in urination
or with changes in voiding habits.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adult Male: 50 – 100 mg injected IM every 2 to 3 days or as directed by physician.
PRESENTATION
Testosterone Propionate 100 mg/ml, 10ml multiple dose vial.
STORAGE
Store in a cool dry place between 15 – 25°C. Protect from light.


Reviews