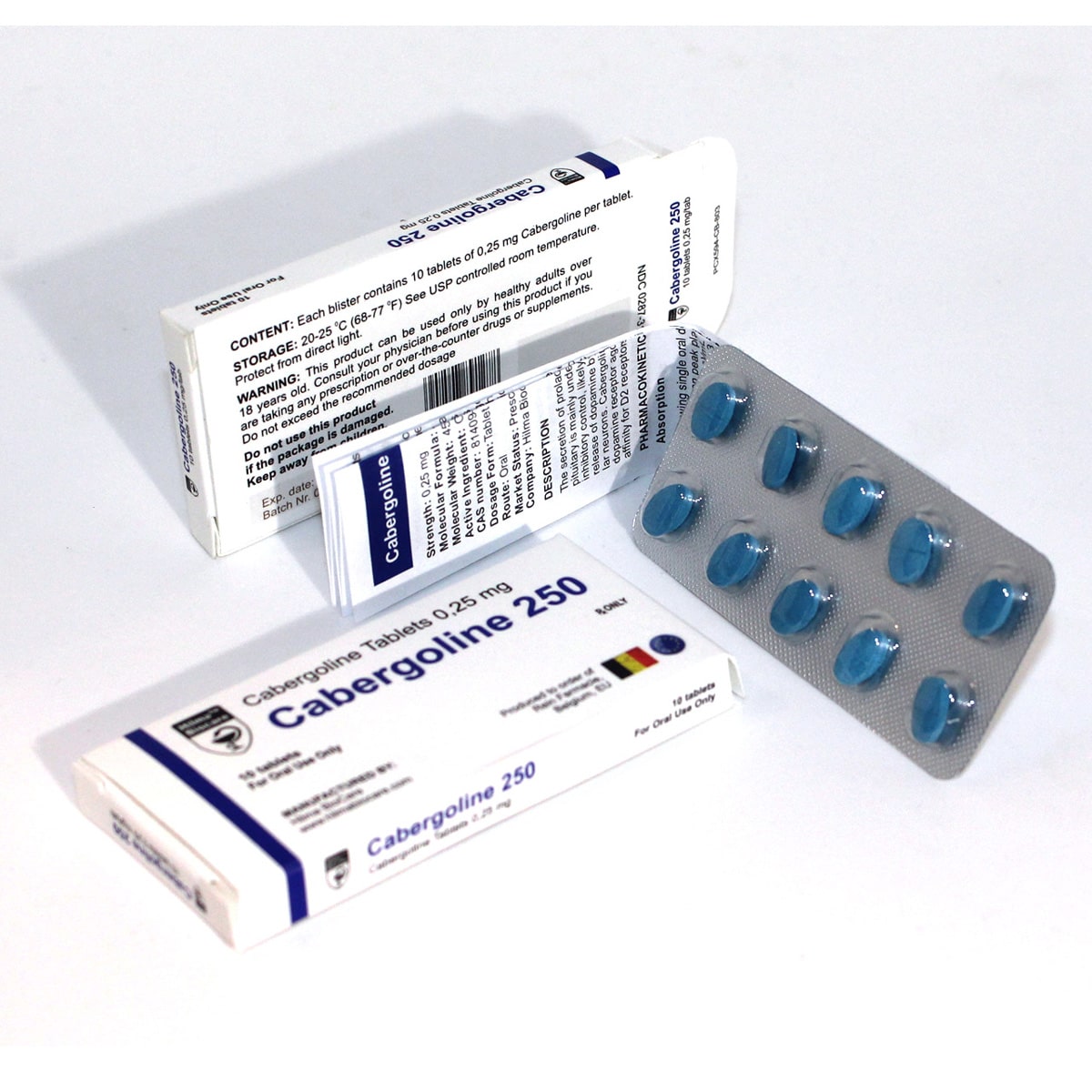
Description
Strength: 0,25 mg
Molecular Formula: China
Molecular Weight: 451.615 g/mol
Active Ingredient: Cabergoline
CAS number: 81409.90-7
Dosage Form: Tablet
Route: Oral
Market Status: Prescription
Company: Hilma Biocare
DESCRIPTION
The secretion of prolactin by the anterior pituitary is mainly under hypothalamic inhibitory control, likely exerted through release of dopamine by tuberoinfundibus lar neurons. Cabergoline is a long-acting dopamine receptor agonist with a high affinity for D2 receptors.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorption
Following single oral doses of 0.5 mg to 1.5 mg mean peak plasma levels of 30 to 70 picograms (pg/mL of cabergoline observed within 2 to 3 hours. A repeatdose study in 12 healthy volunteers suggests that steady-state levels following a once-weekly dosing schedule are expected to be twofold to threefold higher than after a single dose. The absolute bioavailability of cabergoline is unknown. A significant fraction of the administered dose undergoes a first-pass effect. The elimination half-life of cabergoline ranged between 63 to 69 hours. The prolonged prolactin-lowering effect of cabergoline may be related to its slow elimination and long half-life.
Distribution
The drug is extensively distributed throughout the body. Cabergoline is moderately bound (40% to 42%) to human plasma proteins in a concentration-independent manner. Concomitant dosing of highly protein
bound drugs is unlikely to affect itsdisposition.
Metabolism
Cabergoline is extensively metabolized. predominately via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond or the urea moiety. Cytochrome P-450 mediated metabolism appears to be minimal, Hydrolysis of the acylurea or urea moiety abolishes the prolactin-lowering effect of cabergoline, and major metabolites identified thus far do not contribute to the therapeutic effect.
Excretion
After oral dosing of radioactive cabergoline to five healthy volunteers, approximately 22% and 60% of the dose was excreted within 20 days, respectively. Less than 4% of the dose was excreted unchanged in the urine. Nonrenal and renal clearances for cabergoline are about 3.2 L/min and 0.08 L/min, respectively. Urinary excretion in hyperprolactinemic patients was similar.
Pharmacodynamics
Dose response with inhibition of plasma prolactin, onset of maximal effect, and duration of effect has been documented following single cabergoline doses to healthy volunteers (0.05 to 1.5 mg) and hyperprolactinemic patients (0.3 to 1 mg). In volunteers, prolactin inhibition was evident at doses >0.2 mg, while doses > 0.5 mg caused maximal suppression in most subjects. Higher doses produce prolactin suppression in a greater proportion of subjects and with an earlier onset and longer duration of action. In 12 healthy volunteers, 0.5, 1, and 1.5 mg doses resulted in complete prolactin inhibition, with a maximum effect within 3 hours in 92% to 100% of subjects after the 1 and 1.5 mg doses compared with 50% of subjects after the 0.5 mg dose. In hyperprolactinemic patients (N=51). the maximal prolactin decrease after a 0.6 mg single dose of cabergoline was comparable to 2.5 mg bromocriptine: however, the duration of effect was markedly longer (14 days vs. 24 hours).
The time to maximal effect was shorter for bromocriptine than cabergoline (6 hours vs. 48 hours). In 72 healthy volunteers, single or multiple doses (up to 2 mg) of cabergoline resulted in selective inhibition of prolactin with no apparent effect on other anterior pituitary hormones (GH, FSH, LH, ACTH, and TSH) or cortisol.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cabergoline tablets are indicated for the treatment of hyperprolactinemic disorders, either idiopathic or due to pituitary adenomas, specifically:
• Lactation suppression
• Hyperprolactinemia
• Adjunctive therapy of prolactinproducing pituitary gland tumors (prolactinomas);
• Monotherapy of Parkinson’s disease in the early phase;
• Combination therapy, together with levodopa and a decarboxylase inhibitor such as carbidopa, in progressive-phase Parkinson’s disease;
• In some cases also: ablactation and dysfunctions associated with hyperprolactinemia (amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, anovulation, nonpuerperal mastitis and galactorrhea);
• Treatment of uterine fibroids
•Adjunctive therapy of acromegaly. cabergoline has low efficacy in suppressing growth hormone levels and is highly efficient in suppressing hyperprolactinemia that is present in 2030% of acromegaly cases.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of Cabergoline tablets for initiation of therapy is 0.25 mg twice a week. Dosage may be increased by 0.25 mg twice weekly up to a dosage of 1 mg twice a week according to the patient’s serum prolactin level.

Reviews